APENDICITIS
A general surgeon is called to see patients with acute appendicitis. My name is Dr. Allen Alvarez, and one of my roles as a general surgeon is to be available for emergencies that require the management of acute appendicitis. A patient will usually be initially seen at a hospital emergency room and, while “on call,” will contact me at 210-651-0303.
Understanding the Appendix: A Guide
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the beginning of the large intestine. The appendix is typically about 3-4 inches long in the lower right abdomen. It is considered a vestigial organ, meaning it doesn’t have a significant known function in humans. Despite this, it can still cause health issues when inflamed or infected.
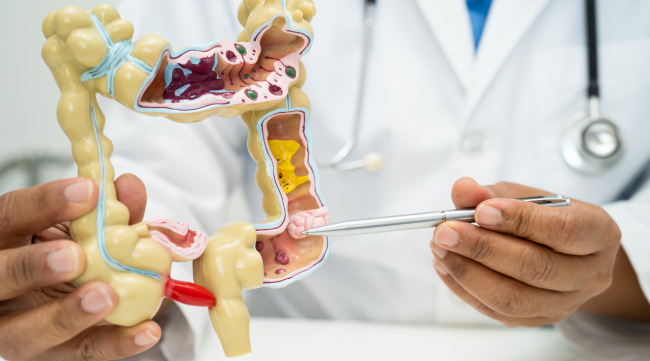
Anatomy of the Appendix:
The appendix is part of the gastrointestinal system and is connected to the cecum, the beginning of the large intestine. Its structure is similar to that of the intestine, consisting of layers of tissue, including mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
Function (or Lack Thereof):
While the specific function of the appendix in humans is not entirely clear, it is believed to have some role in the immune system, specifically in the development and maintenance of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). However, individuals who have had their appendix removed (appendectomy) typically do not experience significant adverse effects on their immune function.
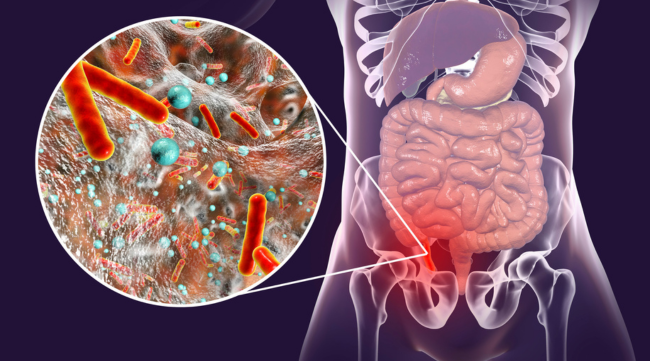

Appendicitis:
An appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the inflamed or infected appendix. It can be performed through traditional open surgery or laparoscopically, which involves smaller incisions and a quicker recovery time. In either case, the goal is to remove the appendix before it ruptures and spreads infection to the abdominal cavity.
Appendectomy:
While the specific function of the appendix in humans is not entirely clear, it is believed to have some role in the immune system, specifically in the development and maintenance of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). However, individuals who have had their appendix removed (appendectomy) typically do not experience significant adverse effects on their immune function.
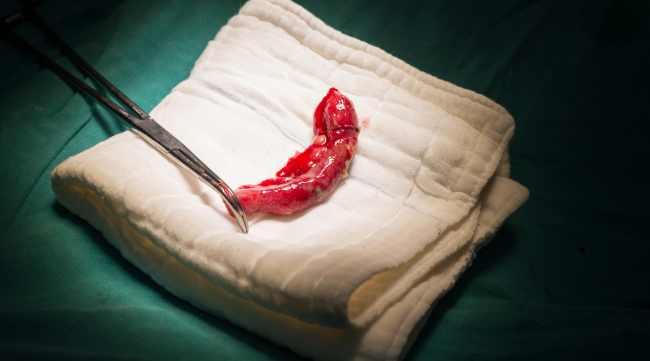
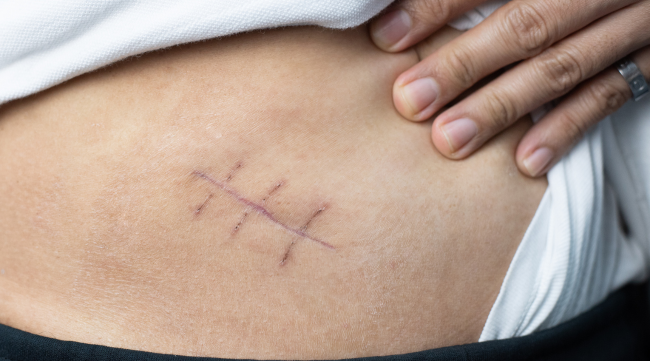
Recovery:
After an appendectomy, most patients can expect to recover within a few days to a week. Pain and discomfort are joint initially but can be managed with medication. It’s important to follow post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon to ensure a smooth recovery and minimize the risk of complications.

Conclusion
While the appendix may not serve a vital function in humans, it can still cause significant health problems when inflamed or infected. Prompt recognition and treatment of appendicitis, typically through surgical removal of the appendix, are crucial for preventing complications and promoting a speedy recovery. For information regarding general surgical needs and those related to bowel obstruction, visit me at ( insert about me on sage website )
